
Composting, as a traditional method of organic waste resource utilization, while possessing environmental advantages, suffers from numerous inherent drawbacks due to technological limitations and environmental conditions. These shortcomings are particularly pronounced in large-scale, standardized production scenarios and must be addressed rationally based on actual needs.
1.Long Composting Cycle and High Environmental Impact
Natural composting typically requires 4-8 weeks to mature, and even high-temperature composting requires 2-4 weeks, far slower than the processing efficiency of professional fertilizer composting equipment. Furthermore, composting effectiveness depends on precise control of temperature, humidity, and carbon-to-nitrogen ratios. Low temperatures and high humidity environments can easily lead to incomplete maturation and the presence of residual pathogens and insect eggs.
2.Unbalanced Nutrients and Difficulty in Precise Control
The nutrient ratios of composting raw materials (straw, manure, etc.) are fixed, making it impossible to adjust the nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium content according to crop needs. This can easily lead to nitrogen deficiency and phosphorus excess. Compared to compound fertilizers produced by NPK fertilizer production lines, compost has a lower nutrient concentration, requiring large-scale application to meet crop requirements.
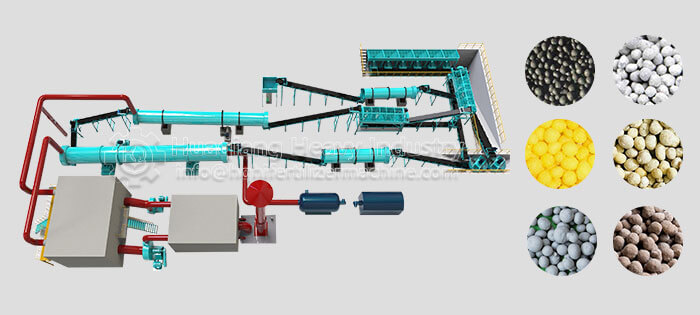
3.Large Footprint and Significant Odor and Pollution Risks
Small-scale composting requires significant space, while large-scale composting, if improperly handled, can release odorous gases such as hydrogen sulfide and ammonia, impacting the surrounding environment. If the raw materials contain heavy metals, antibiotics, or other pollutants, the composting process cannot completely remove them, easily causing secondary soil pollution.
Applicable scenarios are limited. Composting cannot meet the standardized and efficient fertilizer requirements of large-scale, intensive farming. It needs to be combined with specialized fertilizer production equipment for secondary processing to broaden its application scenarios.