
As a compound fertilizer with a synergistic combination of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, NPK fertilizer production requires standardized production lines for large-scale production. Through the coordinated operation of multiple links, NPK fertilizer production lines efficiently transform raw materials into finished products, providing agricultural production with high-quality fertilizers with balanced nutrients.
The core processes of an NPK fertilizer production line revolve around "precise proportioning, uniform mixing, and stable forming." First, in the raw material pretreatment stage, nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilizers (such as urea, monoammonium phosphate) and fillers are crushed and screened to ensure uniform particle size and prevent large particles from affecting subsequent mixing and granulation.
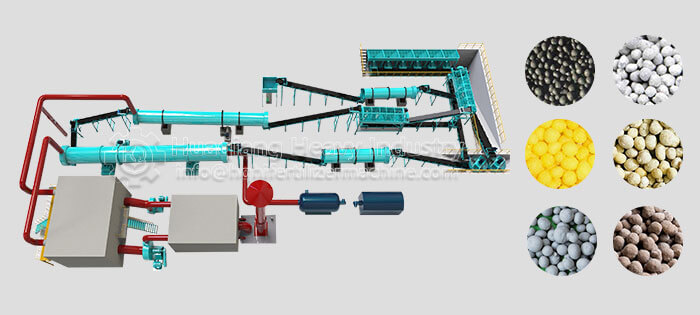
Next, in the mixing stage, an automated batching system precisely measures each raw material according to a preset formula. The raw materials are then fed into a mixing device for thorough mixing. The uniformity of the mixing directly determines the nutrient consistency of the fertilizer. The granulation process is the core of the production line. The raw material mixture is conveyed through a conveyor into the NPK fertilizer granulator machine, where it is tumbled or extruded with the aid of a binder to form granules. The granules' shape and strength must be adapted to subsequent storage and transportation requirements.
After granulation, the wet granules enter a drying and cooling system, where they are dried with hot air to reduce moisture. They are then cooled to room temperature by a cooling device to prevent the granules from clumping and deteriorating. Finally, after screening and grading, qualified granules are packaged, while unqualified granules are crushed and returned to the granulator for reuse, thus achieving resource recycling.