
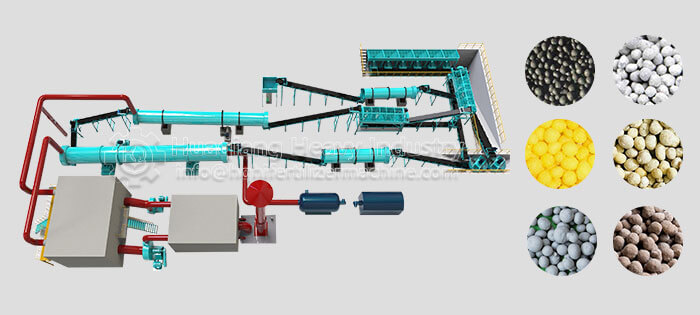
The NPK fertilizer production line is the core process for making compound fertilizers. Handling different materials requires specific processing requirements. Understanding these differences is crucial for improving fertilizer quality and optimizing production efficiency.
1.Nitrogen Source Material Handling Requirements
Nitrogen is essential for plant growth. Common sources include urea, ammonium sulfate, and ammonium nitrate. When processing these, the NPK fertilizer production line needs attention on:
Heat sensitivity: Urea breaks down easily at high temperatures. Keep granulation temperatures strictly between 50-70°C.
Dissolves easily: Urea dissolves readily in water, so adjust binder amounts accordingly.
pH impact: Ammonium nitrogen sources affect mixture pH; neutralize it as needed.
2.Phosphorus Source Material Handling Features
Phosphate fertilizers like superphosphate and ammonium phosphate have special needs:
Fine grind control: Phosphate rock powder needs to be ground fine (80-100 mesh) to boost reaction activity.
Corrosion protection: Superphosphate is corrosive. Equipment needs corrosion-resistant materials.
Moisture control: Ammonium phosphate absorbs moisture easily; keep the environment dry.
3.Potassium Fertilizer Material Handling Points
The main potassium sources, potassium chloride and potassium sulfate, require care:
Hard crystals: Potassium salt crystals are hard; pre-process them to reduce particle size.
Avoid direct mixing: Potassium chloride shouldn't mix directly with ammonium nitrogen sources.
Dissolution control: Potassium salts dissolve well. Adjust granulation process parameters to manage this.
Understanding the different requirements for handling materials in the NPK fertilizer production line helps companies choose suitable equipment, improve formulation processes, boost fertilizer quality, and stay competitive.